Answers
The electric filed lines help to visualize an electric field because they have specific rules. If the lines are dense, it means there's a strong electric filed. In other words, the density of electric filed lines is directly related to the strength of the field.
Therefore, the statement is true.Related Questions
Please help, I need this in by today
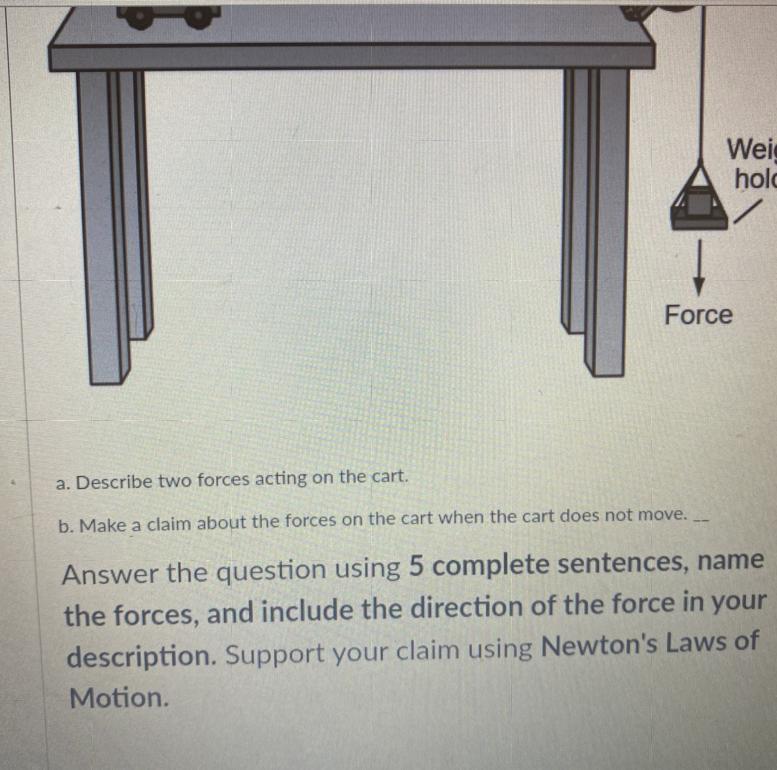
Answers
1.) Force of friction on the cart pointing towards the left
2.) The force of tension of the rope on the cart pointing towards the right
3.) Normal force of the surface on the cart pointing up
4.) Gravitational force of the Earth on the cart pointing downwards
5.) If the cart is not moving, then the friction force acting on the cart must be equal than the tensile force that acts on the cart.
This can be explained using Newton’s First Law: An object at rest will remain at rest, and an object an motion will remain in motion unless acted upon by another force.
(However you’re really only looking at the first part)
Explanation:
Hmm, it is a little difficult to see since the top of the picture is cut off.
There are a few things I will assume:
1.) There is a cart attached to a rope/string, with no other object present other than the weight on the right
2.) You are working with friction
A spring stretches 5 cm when a 300-N mass is suspended from it. Calculate the spring constant in N / m .
Answers
Answer:
Spring constant in N / m = 6,000
Explanation:
Given:
Length of spring stretches = 5 cm = 0.05 m
Force = 300 N
Find:
Spring constant in N / m
Computation:
Spring constant in N / m = Force/Distance
Spring constant in N / m = 300 / 0.05
Spring constant in N / m = 6,000
Wha is the definition of health?
Answers
.A glass bottle has a volume of 10 cm³ at 10°C. Calculate its volume when it is heated to 30°C. [Linear expansivity 9.0x10 k ¹]
Answers
The final volume of the glass bottle when heated to 30°C is 10.0018 cm³.
What is the final volume of the glass bottle?The final volume of the glass bottle is calculated by applying the formula for volume expansivity as follows;
ΔV = V₀αΔT
Where
ΔV is the change in volume of the bottleV₀ is the initial volume of the bottleα is the linear expansivityΔT is the change in temperatureThe change in temperature is calculated as;
ΔT = 30°C - 10°C = 20°C
The change in volume of the bottle;
ΔV = 10 cm³ x (9 x 10⁻⁶) x 20°C
ΔV = 1.8 x 10⁻³ cm³
The final volume of the bottle is calculated as follows;
V₂ = V₁ + ΔV
V₂ = 10 cm³ + 1.8 x 10⁻³ cm³
V₂ = 10.0018 cm³
Learn more about volume expansivity here: https://brainly.com/question/29594873
#SPJ1
What is the economic term for the act of sacrificing one good or service to purchase or produce another?
Answers
Answer:
Trade-off. sacrificing one good or service to purchase or produce another.Which statement describes a primary difference between an electromagnetic wave and a mechanical wave
Answers
The primary difference is that electromagnetic waves can propagate through a vacuum or empty space, while mechanical waves require a physical medium to transmit energy.
Difference between an Electromagnet and Mechanical WaveA primary difference between an electromagnetic wave and a mechanical wave is the medium through which they propagate.
Electromagnetic waves can propagate through a vacuum or empty space without requiring a material medium. They are generated by the oscillation and interaction of electric and magnetic fields.
Examples of electromagnetic waves include radio waves, microwaves, infrared, visible light, ultraviolet, X-rays, and gamma rays. These waves can travel through space, air, or other materials, as they do not rely on physical particles to transmit energy.
On the other hand, mechanical waves require a physical medium to propagate. They are disturbances that travel through a material medium, transferring energy from one location to another. Mechanical waves rely on the interaction and displacement of particles within the medium to transmit energy.
Examples of mechanical waves include sound waves, water waves, seismic waves, and waves on a string. These waves cannot travel through a vacuum as they depend on the physical presence and interaction of particles within the medium.
In summary, the primary difference is that electromagnetic waves can propagate through a vacuum or empty space, while mechanical waves require a physical medium to transmit energy.
Learn more about wave here:
https://brainly.com/question/15663649
#SPJ1
A hockey player applies an average force of 80N to a 0.25kg hockey puck for a time of 0.2s. Determine the impulse experienced by the hockey puck.
Answers
Answer:
16 Newton-seconds
Explanation:
Impulse, \(\widehat{J}\), is given by \(\widehat{J}=F\Delta t\), where \(F\) is the magnitude of a force that has been applied for \(\Delta t\) seconds.
Given \(F=80\text{ N}\) and \(\Delta t = 0.2\text{ s}\), we have:
\(\widehat{J}=80 \cdot 0.2 = \boxed{16\text{ Ns}}\)
Answer:
16 Ns
Explanation:
The answer above is correct.
Can blind people dream?
Just wondering because I've always wanted to know.
Answers
Answer:
yea yes they can they lose their retina but they can dream
A small mailbag is released from a helicopter that is rising\ steadily at 2.32 m/s.
(a) After 5.00 s, what is the speed of the mailbag?
(b) How far is it below the helicopter?
(c) What are your answers to parts (a) and (b) if the helicopter is rising steadily at 2.32 m/s?
Answers
Given parameters:
Velocity of the helicopter = 2.32m/s
Time given = 5.00s
Unknown:
a. Speed of the mailbag after 5s
b. How far is the mail bag below the helicopter
Solution:
In this problem, we must apply the appropriate motion equation to solve.
For a;
v = u + gt
v is the velocity of the mail bag
u is the initial velocity
g is the acceleration due to gravity
t is the time taken
Notice that the initial velocity of the mail bag is 0;
V = 0 + 9.8 x 5 = 49m/s
For b;
Using;
h = ut + \(\frac{1}{2}\) gt²
where u is 0;
h = \(\frac{1}{2}\) x 9.8 x 5² = 122.5m
(The question and setup are below)


Answers
The gauge pressure at bottom of vaccine solution will be 16 kPa
Positive pressure is another name for gauge pressure. When a system's internal pressure exceeds that of its surroundings, it is said to be under positive pressure. Any leak that develops in the positively pressured system will therefore escape into the outside world. In contrast, a negative pressure chamber draws air into it.
Given As seen in the illustration, a syringe is held vertically. The container carries a 3 cm tall column of vaccine solution and has an open inner diameter of 1 cm. The needle contains a 2 cm column of vaccine solution and has an open inner diameter of 0.5 mm. At the needle's open end, the solution is exposed to the air. The vaccination solution has a density of 1200 kg/m3.
We have to find the gauge pressure at bottom of vaccine solution
Since the 5N force is applied to vaccine solution the pressure exerted will be much more
Hence the gauge pressure at bottom of vaccine solution will be 16 kPa
Learn more about gauge pressure here:
brainly.com/question/25736513
#SPJ10
An artillery shell is fired at a target 200 m above the ground. When the shell is 100 m in the air, it has a speed of 100 m/s. What is its speed when it hits its target?
Answers
The speed of the artillery shell when it hits its target is 100 m/s.
Given:
Initial vertical displacement (y) = 200 m
Vertical displacement at 100 m in the air (y') = 100 m
Final velocity in the vertical direction (vy') = 0 m/s (at the highest point of the trajectory)
Using the equation for vertical displacement in projectile motion:
y' = vy^2 / (2g),
where g is the acceleration due to gravity (approximately 9.8 m/s^2), we can solve for the initial vertical velocity (vy).
100 m = vy^2 / (2 * 9.8 m/s^2),
vy^2 = 100 m * 2 * 9.8 m/s^2,
vy^2 = 1960 m^2/s^2,
vy = sqrt(1960) m/s,
vy ≈ 44.27 m/s.
Now, since the horizontal motion is independent of the vertical motion, the horizontal speed of the shell remains constant throughout its trajectory. Therefore, the speed of the shell when it hits its target is 100 m/s.
Hence, the speed of the artillery shell when it hits its target is 100 m/s.
For more such questions on acceleration:
https://brainly.com/question/460763
#SPJ8
Find the charge on capacitor, C2 , in the diagram below if V_ab=24.0 volts,〖 C〗_1=6.00 μF,〖 C〗_2= 3.00 μF,and C_3=10.0 μF.
Answers
The charge on the capacitor 2 (C₂) is 48μF.
Explanation of the circuit diagram
In the circuit diagram, C₁ and C₂ are in series connection, while C₃ is parallel to C₁ and C₂.
Same charge flows in a series arrangement (charge on C₁ = charge on C₂).Same voltage flows in a parallel arrangement (voltage on C₁, C₂ = voltage on C₃).Charge on capacitor C₁ and C₂\(Q_1 = Q_2 = Q\\\\V = \frac{Q}{C_1} + \frac{Q}{C_2} \\\\V = Q(\frac{1}{C_1} + \frac{1}{C_2} )\\\\Q = V (\frac{C_1C_2}{C_1 + C_2} )\\\\Q = 24 \times (\frac{6 \times 10^{-6} \times 3 \times 10^{-6}}{6\times 10^{-6} \ + \ 3 \times 10^{-6}} )\\\\Q = \frac{4.32 \times 10^{-10}}{9\times 10^{-6}} \\\\Q = 48 \ \mu C\)
Thus, the charge on the capacitor 2 (C₂) is 48μF.
Learn more about charge on capacitor here: brainly.com/question/13578522
Which kind of wave interaction is shown?
Answers
Answer:
where?
Explanation:
ill edit my answer when see it
A car, initially at rest, accelerates at 5.70 m/s2 for 6.6 s. How far did it travel in this time?
Answers
In order to calculate the displacement during this time, we can use the formula below:
\(\Delta S=V_0t+\frac{at^2}{2}\\\)So, using the initial velocity V0 = 0, acceleration a = 5.7 m/s² and time t = 6.6 s, we have:
\(\begin{gathered} \Delta S=0+\frac{5.7\cdot6.6^2}{2}\\ \\ \Delta S=124.15\text{ m} \end{gathered}\)Therefore the displacement is 124.15 meters.
P2: Explain in detail - How can the motion of an object that is not moving change? (What are the different ways a static object can change its movement?)
Answers
Inertia: tendency of an object to resist changes in its velocity. An object at rest has zero velocity - and (in the absence of an unbalanced force) will remain with a zero velocity. Such an object will not change its state of motion (i.e., velocity) unless acted upon by an unbalanced force.
Many of the important discoveries of genetics and inheritance came from these:
fruit flies
zebras
enzymes
Answers
Answer:
fruit flies
Explanation:
luv you <3
A motorcycle stoop is at a traffic light, when the light turns green, the motorcycle accelerates to a speed of 78 km/h over a distance of 50 m. What is the average acceleration of the motorcycle over this distance?
Answers
The average acceleration of the motorcycle over the given distance is approximately 9.39 m/s².
To calculate the average acceleration of the motorcycle, we can use the formula:
Average acceleration = (final velocity - initial velocity) / time
First, let's convert the final velocity from km/h to m/s since the distance is given in meters. We know that 1 km/h is equal to 0.2778 m/s.
Converting the final velocity:
Final velocity = 78 km/h * 0.2778 m/s = 21.67 m/s
Since the motorcycle starts from rest (initial velocity is zero), the formula becomes:
Average acceleration = (21.67 m/s - 0 m/s) / time
To find the time taken to reach this velocity, we need to use the formula for average speed:
Average speed = total distance/time
Rearranging the formula:
time = total distance / average speed
Plugging in the values:
time = 50 m / 21.67 m/s ≈ 2.31 seconds
Now we can calculate the average acceleration:
Average acceleration = (21.67 m/s - 0 m/s) / 2.31 s ≈ 9.39 m/s²
To learn more about acceleration
https://brainly.com/question/2303856
#SPJ8
4. Calculate the kinetic energy of a 4.7 kg object moving at a speed of 7 m/s. SHOW YOUR WORK
Answers
Answer:
\(\boxed {\boxed {\sf 115.15 \ J}}\)
Explanation:
Kinetic energy is the energy an object possesses due to motion. It is calculated with the following formula.
\(E_K= \frac{1}{2} mv^2\)
The mass of the object is 4.7 kilograms. The velocity of the object is 7 meters per second.
m= 4.7 kg v= 7 m/sSubstitute the values into the formula.
\(E_K= \frac{1}{2} (4.7 \ kg)(7 \ m/s)^2\)
Solve the exponent.
(7 m/s)²= 7 m/s * 7 m/s = 49 m²/s²\(E_K= \frac{1}{2} (4.7 \ kg)(49 \ m^2/s^2)\)
Multiply the numbers together.
\(E_K = 2.35 \ kg * 49 \ m^2/s^2\)
\(E_K= 115.15 \ kg*m^2/s^2\)
Convert the units. 1 kilogram square meter per square second is equal to 1 Joule.
\(E_K= 115.15 \ J\)
The object has 115.15 Joules of kinetic energy.
Explanation:
Kinetic energy, \(\textbf{\textit{K}}\) is the energy associated with the state of motion of an object. This implies that as a particle accelerates by an external force, the kinetic energy possessed by the particle itself increases. Similarly, the kinetic energy of a particle decreases as an external force decelerates the particle and when the particle is stationary, it's kinetic energy is zero.
We account for such a change of kinetic energy as the energy transferred to the particle from an external force or from the particle to an external force, respectively. This transfer of energy, by a force \(\vec{F}\), is defined as the work done, W on the particle by the force \(\vec{F}\). Positive work denotes the energy transferred to the particle whereas negative work is the transfer of energy from the particle.
Hence, it is obvious that the concept of work and kinetic energy are related and this relationship is defined by the work-energy theorem. The theorem states that that the work done, W by all forces acting on a particle (the resultant force) equals the change in the kinetic energy of the particle, formally written as
\(W \ = \ \Delta K \\ \\ W\ = \ K_{\text{final}} \ - \ K_{\text{initial}}\)
Recall the kinematic equation for uniform acceleration,
\({v_{\text{final}}}^{2} \ = \ {v_{\text{initial}}}^{2} \ + \ 2a\Delta x\).
For a moving particle, \(\Delta x \ = \ d\), where \(d\) is the displacement of the particle, and from Newton's second law of motion, we know that the acceleration \(a \ = \ \displaystyle\frac{F}{m}\). Hence,
\({v_{\text{final}}}^{2} \ = \ {v_{\text{initial}}}^{2} \ + \ \displaystyle\frac{2Fd}{m} \\ \\ \displaystyle\frac{1}{2}m{v_{\text{final}}}^{2} \ - \ \displaystyle\frac{1}{2}m{v_{\text{initial}}}^{2}\right) \ = \ Fd\)
Additionally, work done, W on a particle by a constant force is the product of the component of the force in the direction of its displacement and the magnitude of the displacement.
\(W \ = \ Fd\).
Thus,
\(W \ = \ \displaystyle\frac{1}{2}m{v_{\text{final}}}^{2} \ - \ \displaystyle\frac{1}{2}m{v_{\text{initial}}}^{2}\right)\),
in which
\(K_{\text{final}} \ = \ \displaystyle\frac{1}{2}m{v_{\text{final}}}^{2}\) and \(K_{\text{initial}} \ = \ \displaystyle\frac{1}{2}m{v_{\text{initial}}}^{2}\).
Therefore, in general, for a particle of mass m moving with a speed v, the kinetic energy of the particle is defined as
\(K \ = \ \displaystyle\frac{1}{2}mv^{2}\).
Substitute the known quantities into the expression above yields
\(K \ = \ \displaystyle\frac{1}{2}(4.7 \ \text{g})(7 \ \text{m s}^{-1})^{2} \\ \\ K \ = \ 115.15 \ \text{J}\)
Two balls with masses M and m are connected by a rigid rod of length L and negligible mass as shown in Figure. For an axis perpendicular to the rod, Show that this moment of inertia is I=μL 2 , where μ=mM/(m+M).
Answers
Two balls with masses M and m are connected by a rigid rod of length L and negligible mass as shown in Figure. For an axis perpendicular to the rod, The moment of inertia of the system is I = μL^2, where μ = mM/(m+M).
To calculate the moment of inertia (I) of the system, we will consider the individual moments of inertia of both balls and then sum them up.
Identify the individual moments of inertia of both balls.
The moment of inertia of a point mass is given by I = m * r^2, where m is the mass and r is the distance from the axis of rotation. For ball M, the distance from the axis of rotation is L, while for ball m, the distance is 0.
Calculate the moments of inertia of both balls.
For ball M: I_M = M * L^2
For ball m: I_m = m * 0^2 = 0
Sum the individual moments of inertia.
I_total = I_M + I_m = M * L^2 + 0 = M * L^2
Substitute μ with mM/(m+M).
Now, let's rewrite the expression for the moment of inertia using μ = mM/(m+M). We need to express M in terms of μ.
M = μ(m+M)/m
Solve for M.
M * m = μ(m+M)
M * m - μM = μm
M(m - μ) = μm
M = μm/(m - μ)
Substitute M in the expression for I_total.
I_total = (μm/(m - μ)) * L^2
Simplify the expression.
I = μL^2
For more such questions on moment of inertia, click on:
https://brainly.com/question/3406242
#SPJ11
The probable question may be:
Two balls with masses M and m are connected by a rigid rod of length L and negligible mass as shown in Figure. For an axis perpendicular to the rod, Show that this moment of inertia is I=μL^2 , where μ=mM/(m+M)

A supernova remnant is now 4.55 pc in radius and is expanding at 3,350 km/s. Approximately how many years ago did the supernova occur?
Answers
Based on the diagram, why does the lightbulb light when the loop rotates, and what is the energy change involved?
When the wire moves in an electric field, electrons in the wire move and become mechanical energy. The mechanical energy causes the light to glow. Electrical energy used to rotate the loop is converted to light energy.
When the wire moves in an electric field, electrons in the wire move and become mechanical energy. The mechanical energy causes the light to glow. Electrical energy used to rotate the loop is converted to light energy.
When the wire moves in a magnetic field, electrons in the wire move and become an electric current. The current causes the light to glow. Mechanical energy used to rotate the loop is converted to electrical energy.
When the wire moves in a magnetic field, electrons in the wire move and become an electric current. The current causes the light to glow. Mechanical energy used to rotate the loop is converted to electrical energy.
When the wire moves in an electric field, electrons in the wire move and become mechanical energy. The mechanical energy causes the light to glow. Mechanical energy used to rotate the loop is converted to electrical energy.
When the wire moves in an electric field, electrons in the wire move and become mechanical energy. The mechanical energy causes the light to glow. Mechanical energy used to rotate the loop is converted to electrical energy.
When the wire moves in a magnetic field, electrons in the wire move and become an electric current. The current causes the light to glow. Mechanical energy used to rotate the loop is converted to light energy.
Answers
Answer:
Based on the information provided, the lightbulb lights when the loop rotates because the movement of the wire in an electric or magnetic field causes electrons in the wire to move and become either mechanical energy or an electric current. This energy causes the light to glow. The energy change involved is the conversion of electrical or mechanical energy used to rotate the loop into either light or electrical energy
Explanation:
Which one is the definition of the transverse wave?
Select one:
a. Particle oscillation is parallel to the direction of wave velocity.
b. Particle motion is perpendicular to the direction of wave propagation.
c. Wave carries the particles in parallel direction from one region to another
d. Wave transports energy but not matter from one region to another region.
Answers
b. Particle motion is perpendicular to the direction of wave propagation is the definition of a transverse wave. In transverse waves, the particles of the medium oscillate perpendicular to the direction of the wave's motion. Examples of transverse waves include electromagnetic waves (such as light) and waves on a string.
A man consumes 2985 kcal of food in one day, converting most of it to body temperature. If he loses half this energy by evaporating water (through breathing and sweating), how many kilograms of water evaporate?
Answers
Answer:
m = 2.76 kg
Explanation:
The mass of water evaporated can be found by using the following formula:
\(Q = mH\\\\m = \frac{Q}{H}\)
where,
m = mass of water evaporated = ?
Q = Energy used = \(\frac{1}{2}(2985\ kcal) = (1492.5\ kcal)(\frac{4.184\ KJ}{1\ kcal})\) = 6244.62 KJ
H = Latent heat of vaporization of water = 2260 KJ/kg
Therefore,
\(m = \frac{6244.62\ KJ}{2260\ KJ\kg}\)
m = 2.76 kg
Which statement about quadrilaterals is true?
1) All quadrilaterals have four right angles.
2) All quadrilaterals have equal sides. 3) All
quadrilaterals have four sides. 4) All
quadrilaterals are parallelograms.
Answers
All quadrilaterals have four sides. So, the correct option is (C).
What is Quadrilateral?A quadrilateral is defined as a closed shape and a type of polygon that has four sides, four vertices and four angles that are formed by joining four non-collateral points. The sum of the interior angles of a quadrilateral is always equal to 360 degrees.
The formula for the interior angle sum of a polygon is (n - 2) × 180, where n equals the number of sides of the polygon. There are six basic types of quadrilaterals, these are:
TrapeziumParallelogramRectangleRhombusSquareKiteA quadrilateral is a closed figure with 4 sides where a figure with four sides and the figure has a set of parallel sides and does not contain any right angles.
Thus, all quadrilaterals have four sides. So, the correct option is (C).
Learn more about Quadrilateral, here:
https://brainly.com/question/29934440
#SPJ2
How are vibration waves and energy related to sounds
Answers
In electromagnetic waves, energy is transferred through vibrations of electric and magnetic fields. ... In sound waves, energy is transferred through vibration of air particles or particles of a solid through which the sound travels.
Answer:
because vibration waves are made by sound
Which statements describe scientific laws but not theories or hypotheses? Check all that apply.
They are likely to change as new evidence is discovered.
They do not provide explanations for why they are true.
They are considered to be proven facts.
They have not yet been tested.
They are the bases for experiments instead of the results.
Answers
Answer:
B. They do not provide explanations for why they are true.
C. They are considered to be proven facts.
Explanation:
edge 2021
The statements describe scientific laws but not theories or hypotheses are they do not provide explanations for why they are true and they are considered to be proven facts.
What are scientific laws?The law given by the experimenters or scientists after years of observations and experiments based on the scientific reasons are called scientific laws.
The laws are not the proven facts. They even don't explain why the scientific laws are true.
Thus, the correct option is B and C.
Learn more about scientific laws
https://brainly.com/question/15189105
#SPJ2
write down the value of
920 kg in g
Answers
Answer:
920000
Explanation:
Each kg contains 1,000 grams
Researchers studying the possible effects of “heading” a soccer ball--hitting it with the head--use a force plate to measure the interaction force between a ball and a hard surface. (Figure 1) shows smoothed data of the force when a 430 g
soccer ball is fired horizontally at the force plate with a speed of 15 m/s
With what speed does the ball rebound from the plate?

Answers
The speed of the ball rebounding from the plate is approximately 13.2 m/s.
According to the graph, the greatest force exerted by the football on the force plate during impact is around 1900 N. The ball comes to a halt on the force plate before rebounding.
The kinetic energy of the ball before impact equals the kinetic energy of the ball after the rebound, according to the law of conservation of energy.
The speed of the ball rebounding can be calculated using the formula:
(1/2)mv²= (1/2)mv_0²
where m is the mass of the ball (0.43 kg), v is the speed of the ball rebounding, and v_0 is the initial speed of the ball (15 m/s).
Solving for v, we get:
v = sqrt(v_0² - (2F/m))
where F is the maximum force exerted on the force plate (1900 N).
Plugging in the values, we get:
v = sqrt(15² - (2*1900/0.43)) ≈ 13.2 m/s
Therefore, the speed of the ball rebounding from the plate is approximately 13.2 m/s.
learn more about speed here
https://brainly.com/question/13943409
#SPJ1
A jet, sitting on the runway, takes off and accelerates at 8.0 m/s for 16s. How far did the jet travel down the runway?
Answers
Answer:
2.4 m/s". 1
Explanation:
A jet with mass m = 8 x 10* kg jet accelerates down the runway for takeoff at 2.4 m/s". 1
A 2.0-m wire carrying a current of 0.60 A is oriented parallel to a uniform magnetic field of 0.50 T. What is the magnitude of the force it experiences
Answers
Answer:
The force experienced is 0.6 N
Explanation:
Given data
length of wire L= 2 m
current in wire I= 0.6 A
magnetic field B= 0.5
The force experienced can be represented as
\(F= BIL\)
\(F= 0.5*0.6*2\\\F= 0.6 N\)